Curiosity Rover
A science lab on Martian land, Curiosity Rover is about a size of car exploring the Gale Crater on Mars as part of NASA research program MSL.
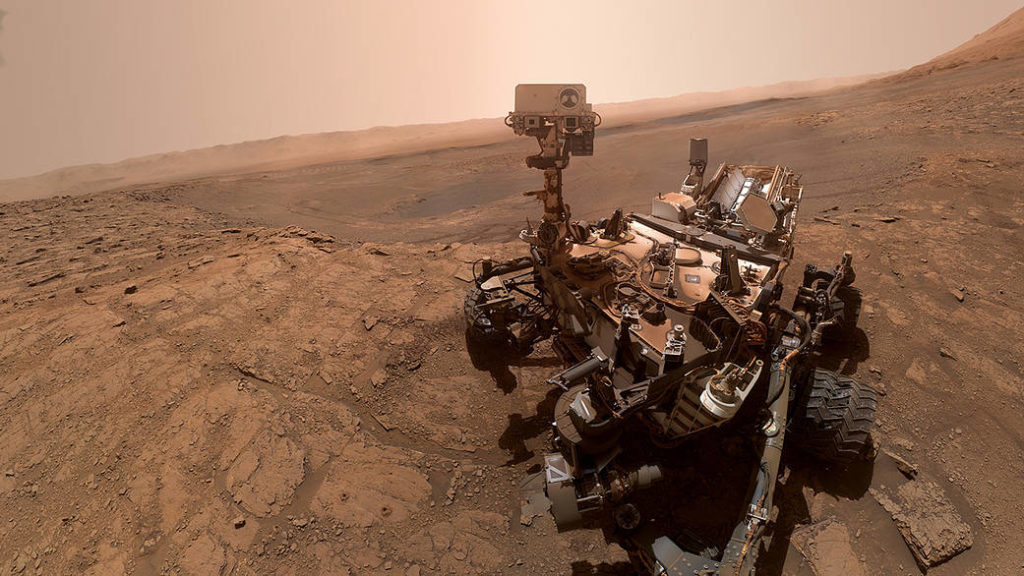

The rover landed on Mars in 2012 with a primary goal to find out if Mars is, or was, suitable for life, to learn more about the Red Planet’s environment, and planetary habitability studies in preparation for future human exploration.
The Rover was launched from Cape Canaveral on 26th November 2011 at 8:32 PM IST (15:02 UTC) landed on Aeolis Palus inside the Gale Crater on 6th August 2012 at 10:47 AM IST(5:17 UTC) on Mars.
Designed to survive for 2 year but the mission was extended indefinitely and in 2018 of March, it celebrated 2000 SOL(Martian days).
Making its way from Gale Crater to Mount Sharp (Aeolis Mons) where it found evidence of past water and geological change.
The rover is still operating in full power as of July 24, 2020.
Size of Curiosity Rover?
Curiosity is about 9 feet 10 inches long by 9 feet 1 inch wide and about 7 feet high. It weighs 900 kilograms. Curiosity’s wheels have a 50.8 cm diameter. The rover size is often refereed as car sized rover.
Goals of Curiosity Rover
- Determine whether life ever arose on Mars.
- Characterize the climate of Mars.
- Characterize the geology of Mars.
- Prepare for human exploration.
These were the primary mission for Curiosity rover, There are still some other objectives too,
- Determine the nature and inventory of organic carbon compounds.
- Identify features that may represent the effects of biological processes.
- Investigate the chemical, isotopic, and mineralogical composition.
- Assess Martian atmospheric evolution processes.
- Interpret the processes that have formed and modified rocks and soils.
- Investigate the chemical building blocks of life.
- Determine present state, distribution, and cycling of water and CO2.
Rover Power Source
Curiosity is powered by a RTG(Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator).
Scientific Instruments
Most of the work is done with the help of high resolution. The rover carries a total off 17 Cameras.
- HazCams-8 ( Hazard Avoidance Cameras)
- NavCams-4 (Navigation Cameras)
- MastCams-2 (Mast Cameras)
- Mahli-1 (Mars Hand Lens Imager)
- MARDI-1 (Mars Descent Imager)
- ChemCam-1 (Chemistry and Camera complex)
Apart from the cameras they are some others instruments too,
- Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS)
- Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS)
- Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin)
- Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM)
- Dust Removal Tool (DRT)
- Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD)
- Dynamic Albedo of Neutrons (DAN)
- Robotic Arm.
Complicated Landing
After 7 months off Space travel final it reached the Red planet on 6th August 2012. Because of Curiosity’s weight, NASA determined using a rolling method with land bags would probably not work.
Instead, the rover went through an extremely complicated sequence of maneuvers to land. Most known as “7 minutes of terror“.
Issues with the Rover
Curiosity had a dangerous computer glitch just six months after landing that put the rover within only an hour of losing contact with Earth forever.
Another small glitch in 2016 briefly stopped science work, but the rover quickly resumed its mission.
Vapors from a wet chemistry experiment filled with a fluid called MTBSTFA contaminated a gas-sniffing analysis instrument shortly after Curiosity landed.
Just in months after landing, NASA noticed damage to the rover’s wheels appearing much faster than expected.
Distance Covered by Curiosity
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover covered over 22.97 Km as of July 24.
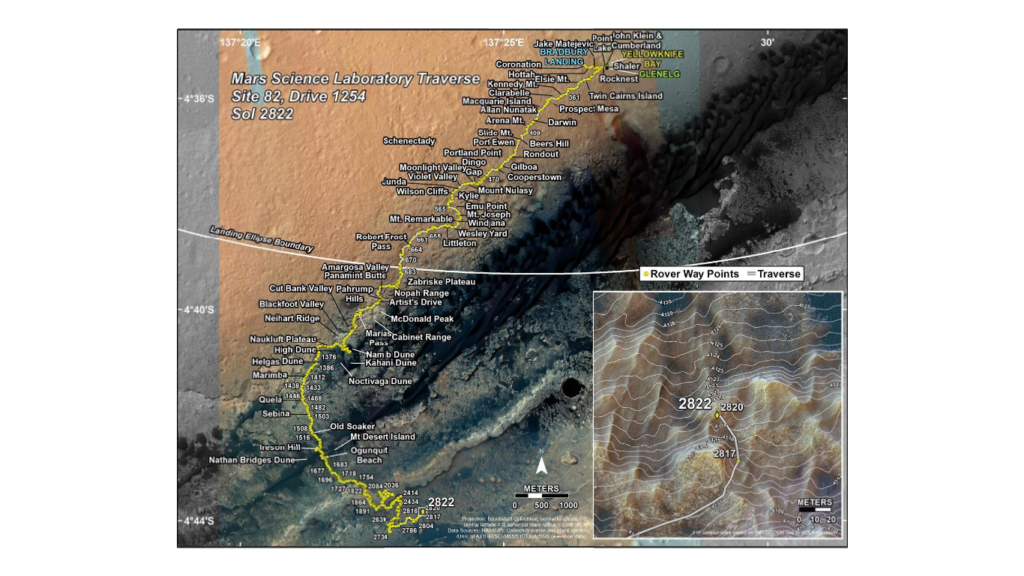
Curiosity’s rover design is served as the basis for Perseverance mission which will carry different scientific instruments that helps for future human exploration.
Source:
- JPL: Mars Science Laboratory / Curiosity Rover
- NASA Solar System Exploration: Mars Science Laboratory / Curiosity
